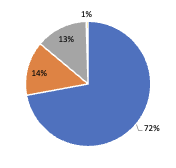
The rising concern of climate change creates the urgency for solutions to counter the increase in the emissions. The economic sector which has the largest share in the greenhouse gas emissions has been the transportation sector. In the US in 2018, the major contributor towards the total greenhouse gas emissions has been the transportation sector with almost 29% of the total share. This included emissions from cars, trucks, ships, trains and planes.

Within the transportation sector, road transport is the major contributor towards the greenhouse gas emissions. It is evident that to reduce the impact of greenhouse gas emissions, transport sector should be redesigned to facilitate vehicles with lower emissions and thus reduce the overall greenhouse gas emissions.
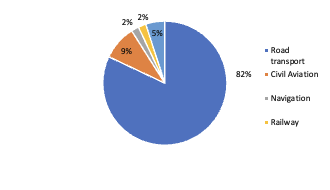
To reduce the amount of the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the transport sector, it is mandatory that strategies are developed to improve the vehicles on road. The strategies may include the following-
- Use of better alternate fuel which emit less emissions on combustion.
- Use of low emission vehicles in the transport sector.
There is a global trend to promote sustainable modes of transport which has resulted in increasing use of Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs), as shown in Figure 3. ULEVs are the vehicles that emit less than 75g of CO2/km and include different classes of vehicles namely Battery electric Vehicles (BEV), electric range-extender vehicles and Plug-in Hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) (2). The different classes of the ULEVs can be described as following-
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)- BEV is a class of electric vehicle which is operated on electricity and has a battery system supporting the electric motors which drive the vehicle. These vehicles have an on-board charger which when connected to an external charger can be used to charge the battery system.
- Electric range extender vehicles- These are the class of vehicles installed with an auxiliary power unit which is used to charge the electric motors which increase the operational range of the vehicles.
- Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)- PHEVs are the vehicles which use a conventional internal combustion engine and battery-powered electric motor.

References
- Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions | US EPA [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 19]. Available from: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions
- Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEVs) [Internet]. [cited 2020 May 30]. Available from: https://www.smmt.co.uk/industry-topics/technology-innovation/ultra-low-emission-vehicles-ulevs/
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Global EV Outlook 2020. Glob EV Outlook 2020. 2020;
- Greenhouse gas emissions from transport in Europe — European Environment Agency [Internet]. [cited 2020 Aug 17]. Available from: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/transport-emissions-of-greenhouse-gases/transport-emissions-of-greenhouse-gases-12
- Fast Facts on Transportation Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Green Vehicle Guide | US EPA [Internet]. [cited 2020 Aug 17]. Available from: https://www.epa.gov/greenvehicles/fast-facts-transportation-greenhouse-gas-emissions


